Recent weeks have seen a convergence of significant discoveries and extreme natural events, spanning from the spread of invasive species to the behavior of interstellar comets. These developments highlight both the escalating impact of climate change and the frontiers of human understanding in physics, mathematics, and astronomy.
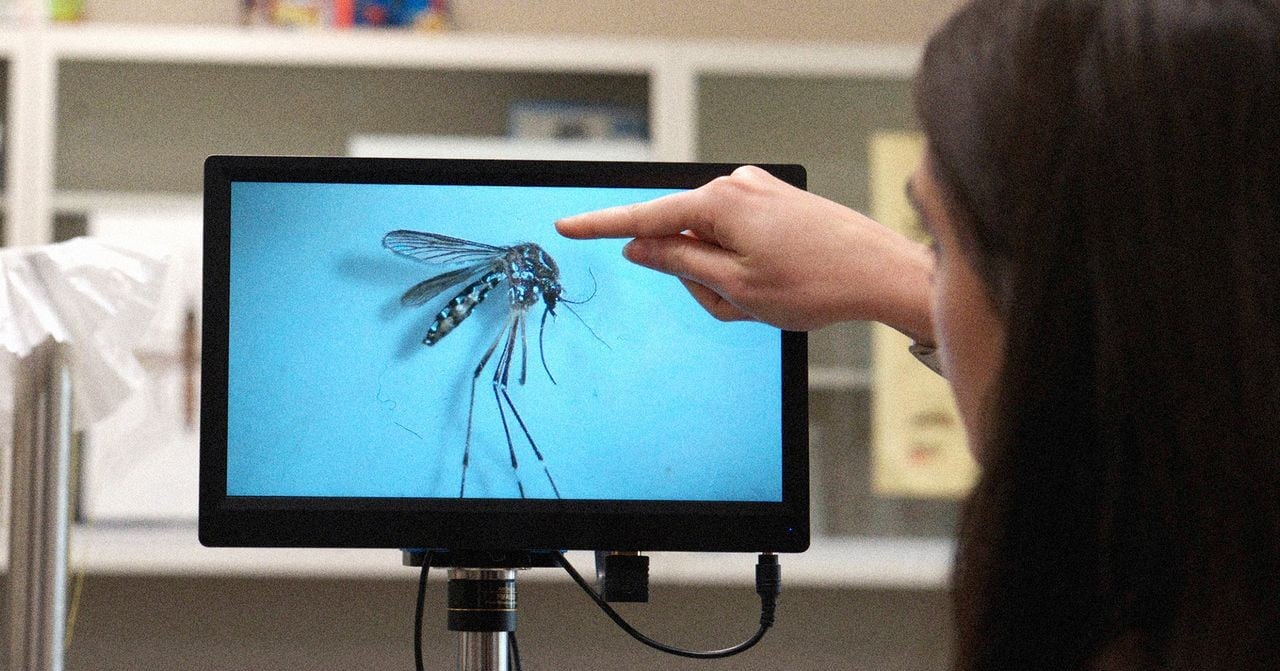
Invasive Mosquitoes Reach the Rocky Mountains
An invasive species of disease-carrying mosquito has expanded its range into the Rocky Mountains, raising concerns about public health. The species, known for transmitting various pathogens, poses a new threat to ecosystems and human populations in the region. This expansion underscores the accelerating rate at which invasive species are colonizing new territories due to climate change and human activity.
Hurricane Melissa: An Unprecedented Storm
Meteorologists are alarmed by the intensity and rapid development of Hurricane Melissa, set to make landfall in Jamaica. The storm’s unusual strength suggests a direct link to warming ocean temperatures, with new research indicating that climate change has made such extreme weather events four times more likely. This highlights the growing frequency and severity of hurricanes fueled by a changing climate.
Quantum Physics: Measuring “Quantumness”
Physicists have developed a thermometer capable of measuring “quantumness” – the degree to which a system exhibits quantum behavior. This breakthrough allows the detection of quantum entanglement without destroying it, opening new avenues for quantum computing and materials science. The device exploits anomalous heat flow to quantify quantum properties, offering a novel approach to understanding the fundamental laws of physics.
Orbital Mechanics: Navigating Space
The principles of orbital navigation differ drastically from terrestrial driving. A spacecraft must slow down to speed up, counterintuitively, due to the laws of gravity and momentum. Understanding this concept is critical for space missions, as precise velocity adjustments are necessary to maintain or alter orbits.
Metal Detectors: Invisible Forces at Work
Metal detectors rely on electromagnetic induction to locate buried metallic objects. When a metal object enters the detector’s field, it disrupts the magnetic flux, triggering an audible signal. This technology exploits the interaction between magnetic fields and conductive materials to identify hidden objects.
Knot Theory: Measuring Complexity
Mathematicians have made progress in quantifying the complexity of knots. The difficulty of untying a knot is directly related to its mathematical structure, with more complex knots requiring more intricate solutions. This research has implications for fields such as polymer physics and DNA sequencing.
Quantum Fractals: The “10 Martini” Proof
A challenging mathematical proof, once offered a reward of ten martinis for its solution, connects quantum mechanics with infinitely intricate structures. The proof uses number theory to explain quantum fractals, demonstrating a deep connection between abstract mathematics and the physical world.
Northern Lights: The Physics Behind the Spectacle
The Northern Lights, or Aurora Borealis, are caused by high-speed solar winds interacting with Earth’s magnetic field. At speeds of up to a million miles per hour, these particles collide with atmospheric gases, creating spectacular light displays. The phenomenon is driven by turbulent magnetic forces and energetic solar activity.
Ocean Waves: The Hidden Mathematics
The mathematics behind ocean waves is notoriously complex, with seemingly simple patterns hiding deep mathematical challenges. Recent advances by Italian mathematicians have brought new clarity to this field, offering insights into fluid dynamics and wave behavior.
Comet 3I/Atlas: Tracking an Interstellar Visitor
Comet 3I/Atlas, an interstellar object passing through our solar system, has reached its closest point to the sun. Astronomers are tracking its trajectory as it moves away from Earth, providing valuable data on objects originating from outside our solar system. The comet’s radio emissions have confirmed its unique composition and origin.
Radio Signals From 3I/Atlas: Confirming its Nature
The first radio signal detected from Comet 3I/Atlas has ended debates about its nature. The signal confirms the comet’s composition and behavior, providing valuable insights into interstellar objects and the conditions in other star systems. The discovery marks a significant step in understanding the origins of comets and the composition of interstellar space.
These developments, spanning from climate-driven extreme weather to the exploration of quantum physics and interstellar objects, underscore the dynamic nature of scientific discovery and the urgent need to address the challenges posed by a changing world